Table of Contents
Introduction
A sprint is a short, time-boxed period during which a team works to complete a set amount of work. Sprints are typically one to four weeks long, but the length can vary depending on the project’s needs. Sprints are a valuable tool for teams looking to improve their productivity, communication, and flexibility. ProductGo is a project management tool that can help you plan and execute sprints more effectively with the user story map feature.
Sprint planning is a crucial aspect of the agile product development process. It allows the product team to convene, establish goals for the upcoming sprint, and determine the tasks necessary to achieve those objectives. Sprint planning promotes focus and productivity within the team, ensuring the product caters to users’ needs effectively.
Sprint Explanation
A. Definition of a sprint
A sprint is a core concept in Agile software development and Scrum framework. It is a set period during which specific work is completed and made ready for review. Sprints begin with a planning meeting where the product owner and development team agree on the work to be accomplished. During a sprint, the team meets daily to discuss their progress and identify any blockers. At the end of each sprint, the team demonstrates their work to stakeholders in a sprint review. The team then uses the feedback from the sprint review to improve their process for the next sprint.
B. Purpose of a sprint
The purpose of a sprint is to deliver a working product increment at the end of each sprint. This allows the team to get feedback from stakeholders early and often, and to make adjustments to the product as needed. Sprints also help to improve team communication and collaboration, as well as to increase focus and productivity.
Here are some of the benefits of using sprints:
- Increased focus and productivity. Sprints help teams focus on a small set of tasks for a short period, which can lead to increased productivity.
- Improved communication and collaboration. Sprints require teams to communicate and collaborate regularly, which can help to improve team relationships and overall project success.
- Greater flexibility and adaptability. Sprints allow teams to adapt to changes in requirements or priorities more easily.
- Early feedback. Sprint reviews provide teams with early feedback on their work, which can help to identify and address any problems early on.
C. Sprint components
The four main components of a sprint are:
- Sprint planning
This is the first meeting of the sprint, and it is where the team determines what work will be done during the sprint. The team works with the product owner to prioritize the backlog, and they then create a sprint backlog that lists all of the tasks that need to be completed. - Daily stand-ups
These are short, daily meetings where team members share updates on their progress, discuss any roadblocks or challenges and align on the day’s priorities. Daily stand-ups foster communication, collaboration, and a shared understanding of the sprint’s status. - Sprint review
At the end of the sprint, the team presents the work they have completed to the product owner and other stakeholders. The stakeholders provide feedback, and the team uses this feedback to improve the product. - Sprint Retrospective
This meeting is held after the sprint review to discuss what went well and what could be improved. The team uses this feedback to plan for the next sprint.
D. The Scrum Framework
The Scrum framework is a lightweight process framework for developing, delivering, and sustaining complex products. It is designed to help teams work together effectively and efficiently.
Sprints are a fundamental part of the Scrum framework. They are short, time-boxed periods during which a team works to complete a specific set of tasks. Sprints typically last one to two weeks, and they are repeated until the entire project is complete.
The relevance of sprints to the Scrum framework is that they provide a way for teams to deliver working software frequently. This allows teams to get feedback from stakeholders early and often, which helps to ensure that the product meets the needs of the users. Sprints also help to improve communication and collaboration between team members, and they can help to reduce risk and improve productivity.
ProductGo Overview
A. Introduction to ProductGo
With ProductGo, user analysis, managing product backlogs, and keeping track of your projects are simplified with its unique functionalities for Portfolios, Projects, and Agile Boards, along with visual models from the user’s perspective.

B. Key features of ProductGo
ProductGo contains 3 main features that could help your team see the big picture of your product from the user’s perspective:
C. Benefits of using ProductGo for sprint planning
By using ProductGo, teams can improve their sprint planning process and deliver better products to their users.
Here are some specific benefits of using ProductGo for sprint planning:
- Improved visibility. ProductGo provides teams with a clear view of the work that needs to be done in a sprint. This helps teams to identify dependencies and to ensure that all of the necessary work is included in the sprint.
- Increased collaboration. ProductGo makes it easy for teams to collaborate on sprint planning. This helps teams to get feedback from each other and to make sure that everyone is on the same page.
- Improved efficiency. ProductGo can help teams to plan sprints more efficiently. This is because ProductGo provides many features that can help teams to automate tasks and to track progress.
- Increased transparency. ProductGo makes it easy for stakeholders to see the team’s progress. This helps to build trust and to ensure that stakeholders are kept up-to-date on the project.
How to Use User Story Map by ProductGo for Sprint Planning
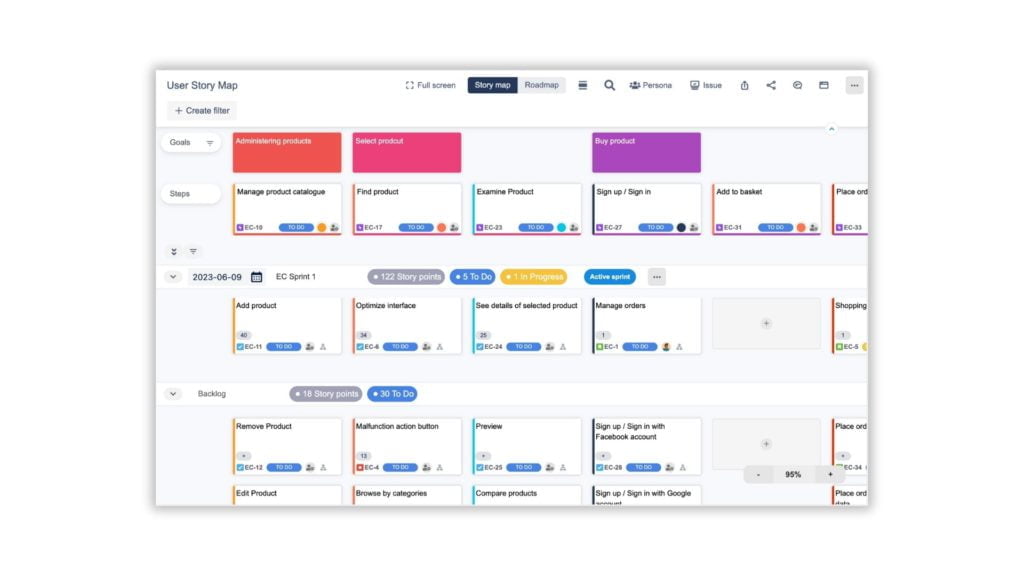
A. Setting up a project in ProductGo
As a Project Owner or Scrum Master, you may need to create a new Scrum project or continue using the existing project in Jira Software to set up for ProductGo.
Here is the instruction to create a new project:
- Go to Jira Software and log in to your account.
- Click on the Projects tab.
- Click on the Create Project button.
- From the Project Template sidebar, click on Software Development and choose Scrum option
- Click on the Use Template button and choose the type of project (team-managed/company-managed)
- Enter the project name and click Next to complete the creation of the project
Download ProductGo by clicking this link or searching for “Agile User Story Maps, Roadmaps & Persona for Jira” on the Atlassian Marketplace
After downloading the app, access it in those ways:
- From app home page
- From project sidebar menu
- From Jira Agile board
B. Defining sprint goals and Epics/Steps
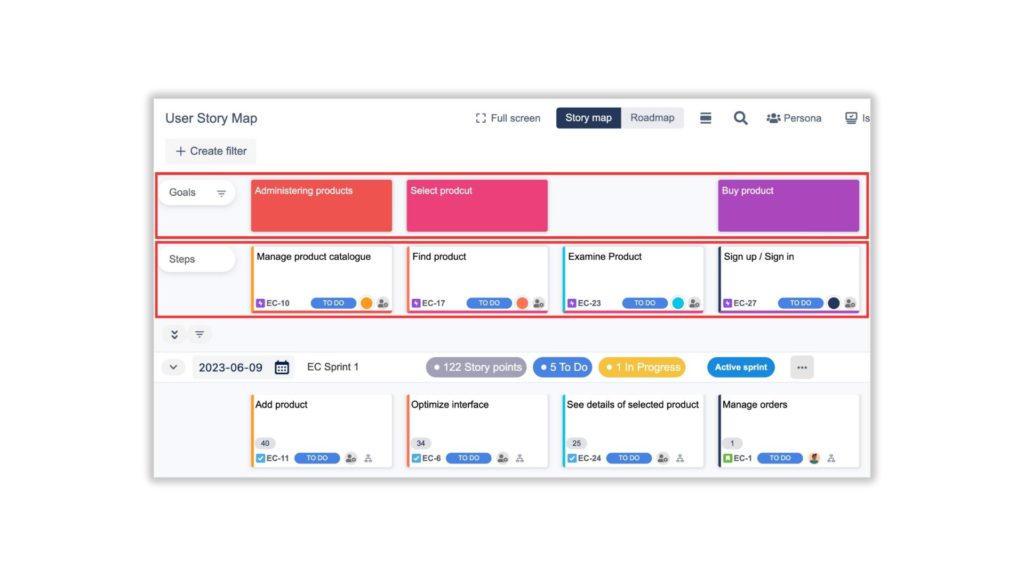
When you have accessibility to the Story Map, start with defining the Goals for the projects by adding cards in the Goals portion of the story map.
Goals are the overall objectives that the product is trying to achieve. They are typically high-level and aspirational, and they provide a framework for the team to work towards.
Below the Goals is the Steps/Epics portion, list down the Steps/Epics by following the above Goals in the story map.
Steps are the lower levels defined under Goals. create the backbone of the map by telling the story or narrative of the user’s journey.
C. Creating a sprint backlog
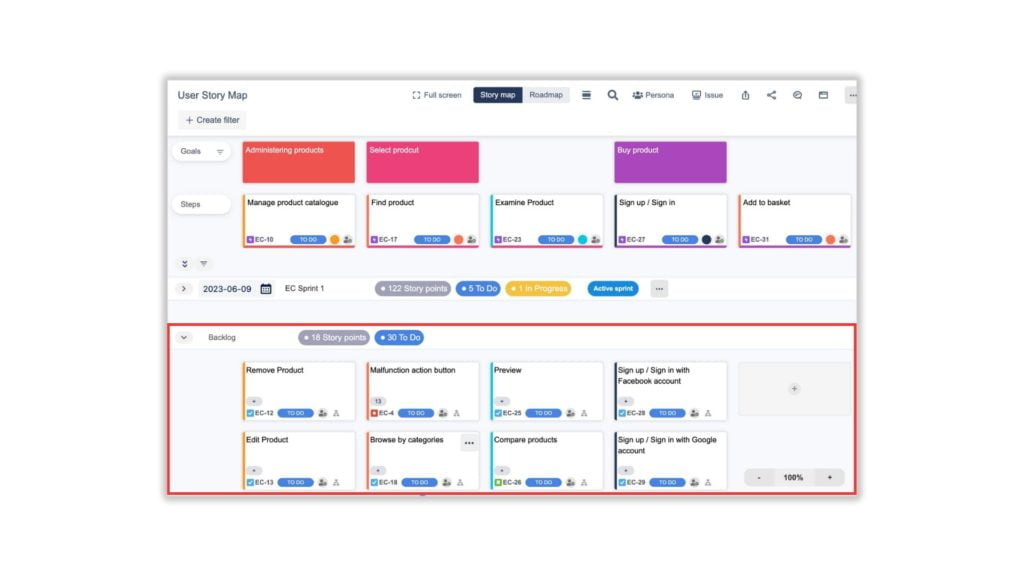
With created Steps/Epics, breaking down them into smaller pieces called User Stories and placing them in the Backlog portion. This is an important step because these Steps/Epics must be split into reasonable and achievable stories and able to be completed in a sprint.
If your User Story Map shows up the Unscheduled/Stories instead of the Backlog portion, follow these steps to change it:
- Click on the Go to admin setting option on the menu button in the top right corner of the User Story Map
- In the Board tab on the left sidebar, turn on the Allow Sprint Swimlane mode option and click on the Save button
- Click on the Back to the story map button
- On the menu button in the top right corner, find the Change swimlane mode option and choose the Sprint option from the list.
Start estimating the story points for each user story after creating it with tools such as Planning Poker. This helps to plan and prioritize work more effectively for the upcoming sprints
D. Planning and allocating sprints
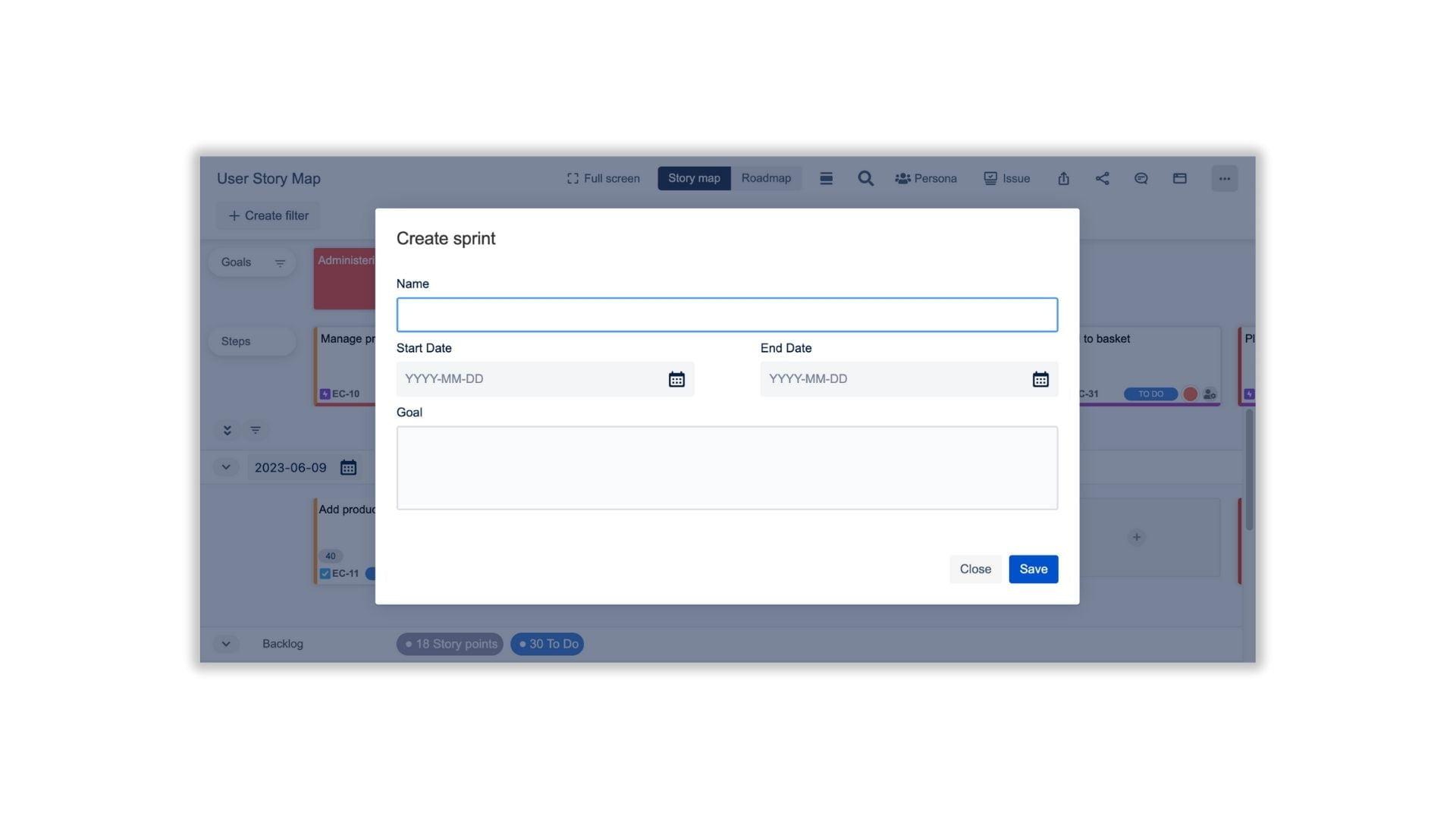
All your available sprints of the project should be shown in the Story Map after the above steps. You also can add a new sprint by following these steps:
- Click on the “+” button lane
- Add required details i.e. Name, Start Date, End Date & Goal
- After adding all the details click on the Save button to save the newly created sprint
After adding the new Sprint to the Story Map, easily drag and drop the stories from the Backlog portion into the intended sprint.
The Product Owner or Scrum Master should allocate resources within a Sprint by considering the story points and the assignee for each task.
E. Completing a Sprint
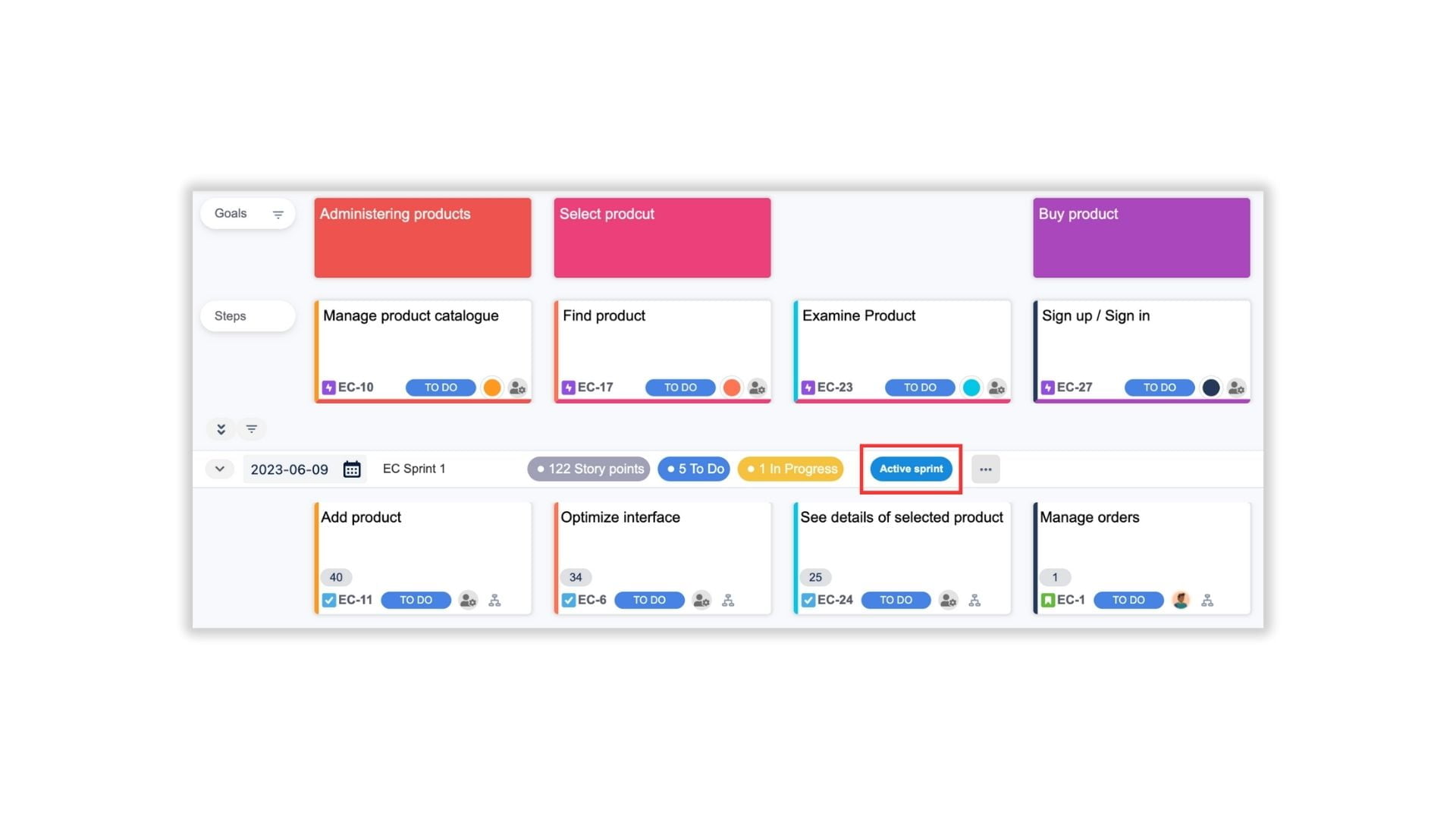
Click on the Start option from the menu button of the Sprint to start a sprint. The Sprint will show the Active Sprint badge.
Your team can now work and update the progress of the Sprint directly on the story map. This could help get everyone on the same page.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sprints are an essential component of the Agile and Scrum framework, facilitating improved productivity, communication, and adaptability within teams. The ProductGo tool enables teams to plan and execute sprints more effectively by providing valuable features such as user story maps, portfolio boards, and product roadmaps. By incorporating User Story Map by ProductGo into their sprint planning process, teams can enhance visibility, collaboration, efficiency, and transparency, ultimately delivering better products that cater to users’ needs.